Sleeping With a Chainsaw: 7 Ways to Stop Pregnancy Snoring Tonight
The title might sound like a joke, but for many partners of pregnant women, it’s a nightly reality. One minute you’re drifting off to sleep next to your beloved partner, and the next, you’re jolted awake by a sound you’ve never heard her make before—a deep, rattling snore that could rival a lumberjack’s. If you’re the one snoring, you might wake up with a sore throat, feeling confused and anything but rested. Welcome to the world of pregnancy snoring, or as it’s clinically known, rhonchopathy.
First, let’s normalize this. Up to 30% of pregnant individuals will develop snoring, especially in the second and third trimesters, even if they’ve never snored a day in their life before. It’s a physical symptom, not a personal failing. It’s caused by a perfect storm of hormonal shifts, increased blood volume, and natural weight gain. While it’s usually a temporary and harmless (albeit loud) annoyance, it’s important to understand why it happens and to know when it might signal a more serious issue. This guide will walk you through the science, provide seven actionable strategies for relief, and empower you and your partner to navigate this challenge as a team, ensuring both of you get the restorative sleep you desperately need.
Why Am I Suddenly Snoring? The Science Behind Pregnancy Rhonchopathy
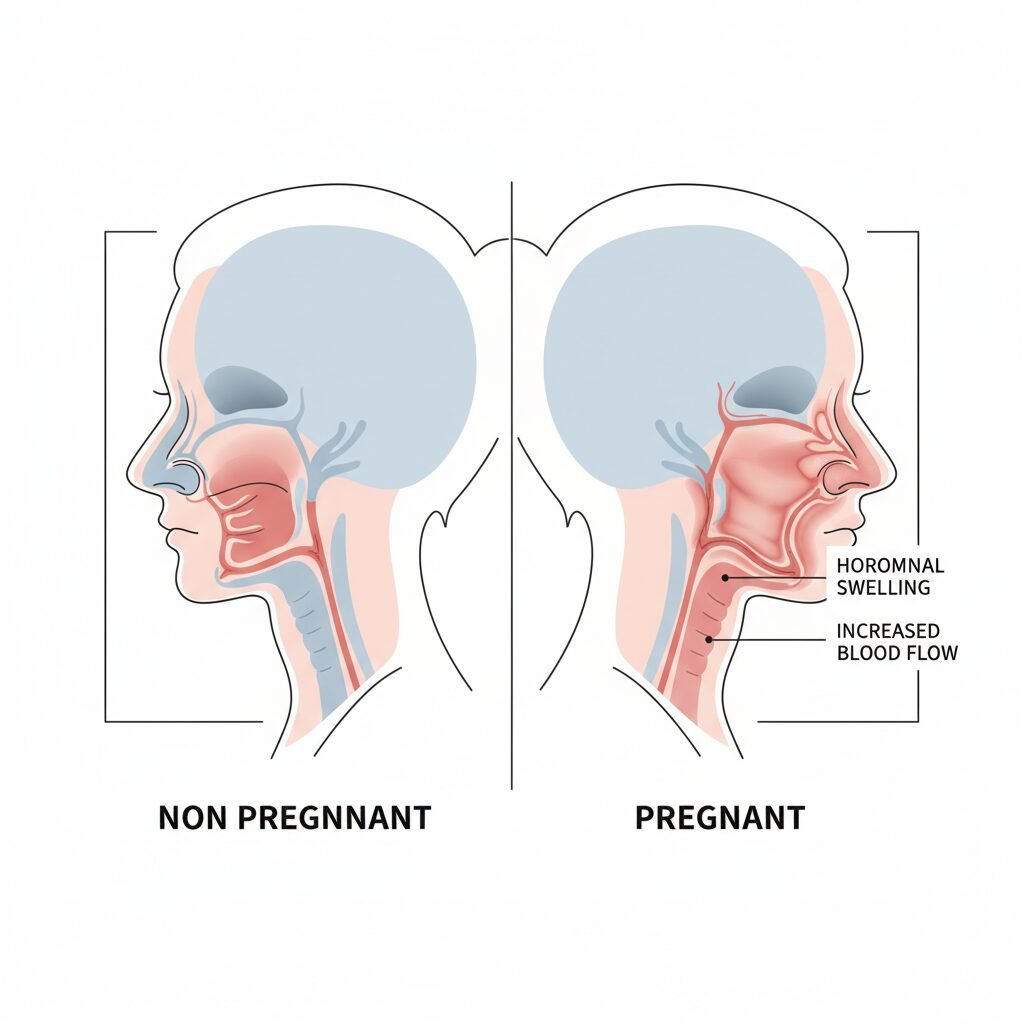
Understanding the ‘why’ behind pregnancy snoring can transform frustration into empathy and empower you to find effective solutions. This isn’t just a random annoyance; it’s a direct result of the incredible physiological changes your body undergoes to grow a new life. Let’s break down the primary culprits:
- Hormonal Havoc: The pregnancy hormones estrogen and progesterone are the main drivers. They cause the mucous membranes lining your nasal passages to swell and increase mucus production. This condition, known as pregnancy rhinitis, creates nasal congestion and stuffiness, narrowing your airway and making it harder to breathe through your nose. When you sleep, your body defaults to mouth-breathing, and the relaxed tissues in your throat are more likely to vibrate, creating the sound of a snore.
- Increased Blood Volume: During pregnancy, your total blood volume increases by nearly 50%. This incredible expansion is necessary to support the placenta and your baby, but it also causes tiny blood vessels, including those in your nasal passages, to swell. This further contributes to the narrowing of your airways.
- Natural Weight Gain: Gaining weight is a healthy and necessary part of pregnancy. Some of this weight gain can result in extra tissue around the neck and throat. This added tissue can put pressure on your airway when you lie down, narrowing the passage and making snoring more likely.
- The Growing Uterus: As your baby grows, your uterus expands upwards, pushing against your diaphragm. This can slightly decrease your lung capacity and alter your breathing mechanics, especially when lying down, potentially contributing to snoring and shortness of breath.
Essentially, your body is creating a smaller, more congested airway, and when air is forced through that narrow space, the surrounding soft tissues vibrate. The result is a snore that can be startling in its intensity. Recognizing these biological factors is the first step toward finding gentle, effective relief.
The 7 Evidence-Based Ways to Reduce Pregnancy Snoring

Now that you understand the causes, let’s focus on the solutions. These seven strategies are safe for both you and your baby and can make a significant difference in your sleep quality—and the decibel level in your bedroom.
-
Master Side-Sleeping
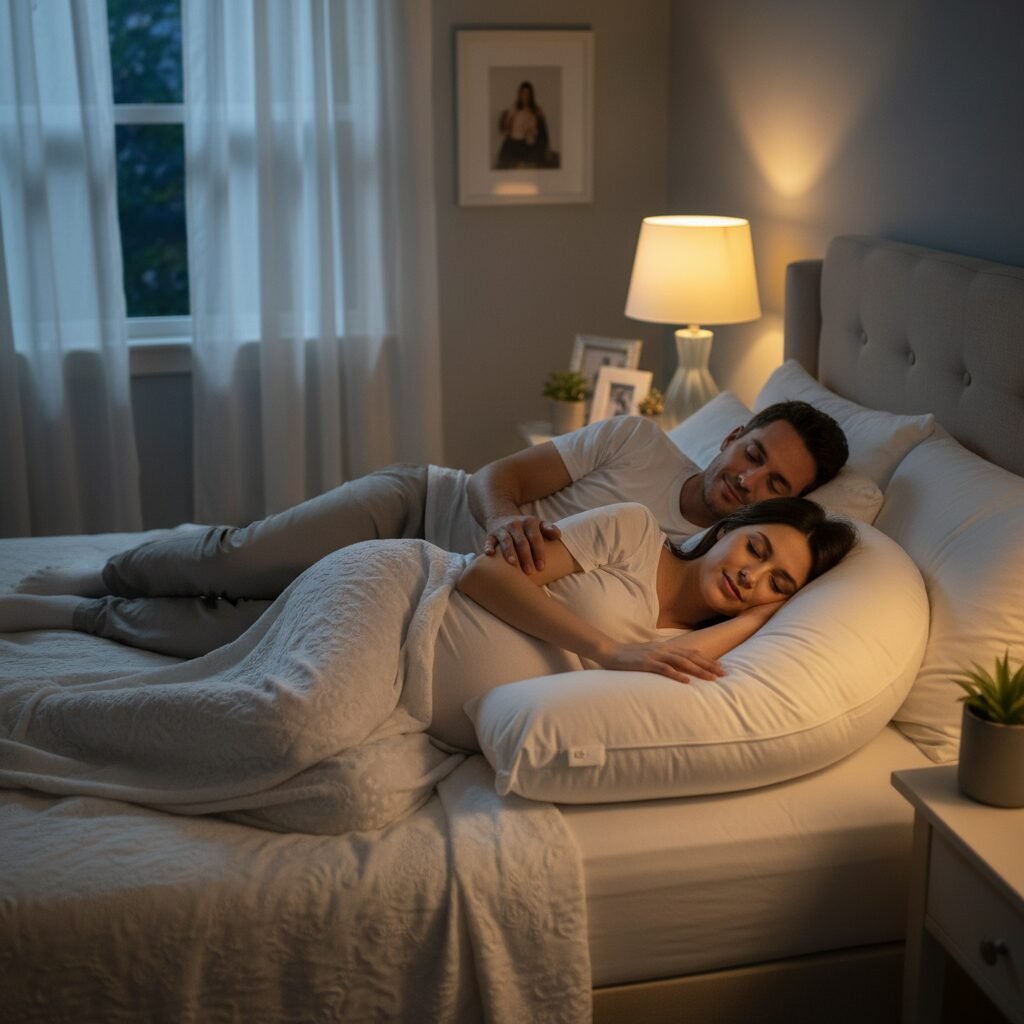
Sleeping on your back allows your tongue and soft palate to collapse to the back of your throat, partially blocking your airway. Sleeping on your side, particularly your left side, is the gold standard for pregnancy sleep. It not only keeps your airway more open but also improves circulation, ensuring optimal blood flow to the placenta. Use pillows to your advantage! A full-body pregnancy pillow can be a game-changer, providing support for your back and belly to keep you comfortably on your side all night.
-
Elevate Your Head
Gravity can be your ally. Propping your head and upper body up with a few extra pillows or a foam wedge can help in two ways. First, it helps drain your nasal passages, reducing congestion. Second, it helps prevent the tissues in your throat from collapsing backward. You don’t need to be sitting bolt upright, but a slight, comfortable incline can significantly open your airway.
-
Hydration and Humidity are Your Best Friends
When you’re dehydrated, secretions in your nose and soft palate become stickier, which can exacerbate snoring. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Additionally, dry air can irritate the membranes in your nose and throat. Running a cool-mist humidifier in your bedroom at night adds moisture to the air, soothing your airways and helping to reduce congestion and inflammation.
-
Address Nasal Congestion Directly
Since nasal stuffiness is a primary cause, targeting it can bring immense relief. Several pregnancy-safe options are available:
- Saline Nasal Sprays: These are simply a sterile saltwater solution. They are completely safe and help to moisturize your nasal passages and clear out mucus.
- Nasal Strips: These external adhesive strips are placed on the bridge of your nose. They gently lift the sides of your nose, opening up the nasal passages to improve airflow.
- Neti Pot: Using a neti pot with distilled, sterile water can effectively flush out your sinuses. Always follow the instructions carefully and never use tap water.
-
Optimize Your Diet and Exercise
What you eat and how you move can impact your breathing. Avoid eating a large, heavy meal within a few hours of bedtime, as this can put pressure on your diaphragm. Some people find that excessive dairy can thicken mucus, so it may be worth seeing if reducing your intake in the evening helps. Regular, moderate, doctor-approved exercise improves muscle tone and circulation, which can help reduce snoring.
-
Create a Sleep-Sanctuary Environment
Good sleep hygiene can improve overall sleep quality and reduce factors that worsen snoring. Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. Identify and eliminate potential allergens like dust, pet dander, or pollen, which can worsen nasal inflammation. Wash your bedding regularly in hot water and consider an air purifier if you’re prone to allergies.
-
Partner Communication and Support
This is a team effort. The snoring person should try these strategies, and the partner can help. A gentle nudge to roll over, a reminder to use the nasal spray, or setting up the humidifier can be acts of love. For the partner, investing in high-quality earplugs or a white noise machine can be a sleep-saver. Open, non-blaming communication is key to navigating this temporary challenge together.
Snoring or Something More? When to Talk to Your Doctor

While most pregnancy snoring is benign, it can occasionally be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition, such as gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, or obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). It is crucial to monitor your symptoms and communicate openly with your healthcare provider. Do not hesitate to bring up your snoring at your next prenatal appointment.
Obstructive sleep apnea is a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. During pregnancy, it can reduce oxygen levels for both mother and baby and is linked to an increased risk of preeclampsia and gestational diabetes. Be aware of the warning signs that differentiate simple snoring from something that warrants immediate medical attention.
| Symptom / Sign | What’s Often Typical (Simple Snoring) | When to Be Concerned (Potential Warning Sign) |
|---|---|---|
| Snoring Pattern | Consistent, rhythmic snoring that may change with position. | Loud, explosive snores interrupted by moments of silence, followed by gasping or choking sounds. |
| Daytime Fatigue | Feeling tired is a normal part of pregnancy. | Extreme, overwhelming daytime sleepiness that interferes with daily activities. Waking up feeling exhausted despite a full night in bed. |
| Headaches | Occasional, mild headaches. | Frequent morning headaches or a persistent, severe headache that doesn’t go away. |
| Blood Pressure | Normal readings at prenatal checkups. | Elevated blood pressure readings (hypertension) noted by your provider. |
| Swelling (Edema) | Mild swelling in the ankles and feet, especially at the end of the day. | Sudden or severe swelling in your hands, face, or around your eyes. |
| Other Symptoms | General pregnancy discomforts. | Vision changes (like seeing spots or blurriness), upper abdominal pain, or sudden weight gain. |
If you experience any of the symptoms in the ‘When to Be Concerned’ column, it is imperative to contact your doctor or midwife immediately. These can be signs of preeclampsia, a serious condition that requires prompt medical care.
For the Partner: How to Cope and Support Her (Without Losing Your Mind)

If you’re the one lying awake next to the ‘chainsaw,’ your feelings of frustration and exhaustion are completely valid. Sleep deprivation is a serious challenge, and it’s okay to admit you’re struggling. However, approaching the situation with empathy and a team-based mindset is crucial for both of you.
Understanding Your Role
Remember, she is not doing this on purpose. Her body is performing a miraculous feat, and snoring is an involuntary side effect. Your role is to be a supportive partner, not a sleep-deprived adversary. Frame your actions and words from a place of care for her and for your collective well-being.
Practical Coping Strategies
- Invest in Noise-Canceling Gear: This is the first line of defense. High-fidelity earplugs (which block noise without being uncomfortable) or noise-canceling headphones paired with a white noise app can be life-savers.
- Create a Buffer Zone: A white noise machine or even a simple fan placed between the two of you can create a consistent, soothing sound that masks the inconsistencies of snoring.
- Go to Bed First: If you’re a lighter sleeper, try going to bed 30-60 minutes before she does. This allows you to fall into a deeper stage of sleep before the snoring potentially begins.
- The Gentle Nudge: If you notice she’s on her back, a very gentle touch on her shoulder and a soft whisper of ‘roll to your side, honey’ is much more effective and loving than an exasperated shove.
- Tactical Retreat (When Necessary): There is no shame in temporarily relocating to a comfortable couch or guest room. Communicate this clearly: ‘I’m going to sleep on the couch so we can both get some rest. I love you.’ It’s not a rejection; it’s a practical solution for a temporary problem.
Your support—whether it’s refilling the humidifier, giving her a back rub to help her relax into a side-sleeping position, or simply offering a hug after a rough night—is an invaluable part of navigating the final stretch of pregnancy together.
Conclusion
Navigating the challenges of pregnancy, including the unexpected arrival of snoring, is a testament to the strength and adaptability of expecting parents. While the sound can be disruptive, remember that for most, it is a temporary phase caused by the incredible work your body is doing. By focusing on practical strategies like optimizing your sleep position, managing congestion, and maintaining open communication, you can significantly reduce the noise and improve sleep for everyone.
Most importantly, stay attuned to your body. Do not dismiss persistent or concerning symptoms. Your healthcare provider is your most important partner in this journey, so keep them informed of any changes you experience. By working together as a couple and with your medical team, you can ensure a safe, healthy, and—with any luck—much quieter path to parenthood.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or before starting any new treatment.







